Are Biomass Boiler Systems Worth It?
Biomass boiler systems cannot be overlooked when it comes to heating efficiency with reduced emissions and low carbon footprint. These units have gained popularity in small businesses and residential communities for their ability to generate pressure waste and manage carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
These boilers come in different sizes, shapes, installation techniques, and fuel types, making it challenging to find the right one. To help you choose, here’s an in-depth guide on how biomass boiler systems work, their efficiency, emissions, and costs.
How Does a Biomass Boiler System Work?
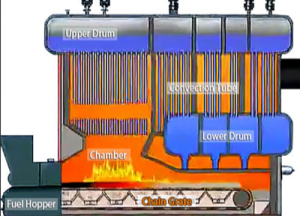
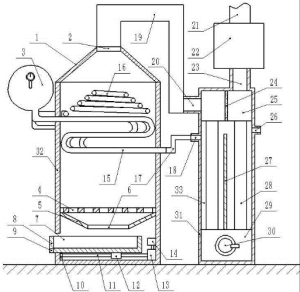
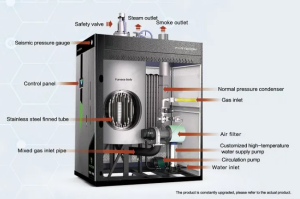
The working principle of biomass boiler systems is similar to conventional boilers, generating heat by burning non-fossil fuels. They are larger than their counterparts because of the substantial fuel volume used in the chamber, occupying more space.
Key Components:
- Fuel hopper for storage
- Combustion chamber where fuel burns
- Heat exchanger that transfers heat to water
- Exhaust system for fumes
- Ash collection system
Three Stage Process:
- Fuel Feeding: The fuel (wood pellets, chips, or logs) is fed into the combustion chamber. Feeders can be automatic, semi-automatic, or manual depending on facility and budget.
- Combustion: When ignited, the fuel produces hot gases that travel through the flue into the heat exchanger chamber, heating water which turns to steam for industrial equipment.
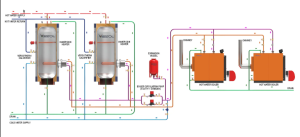
- Byproduct Handling: Ash byproducts collect in a separate tray while remaining heat goes to thermal storage containers (buffer tanks). Maintaining adequate fuel supply reduces transportation costs.
Residential vs Commercial Biomass Boilers
For Homes:
Biomass boiler systems are ideal for homeowners seeking more sustainable, efficient heating. Using natural resources like wood pellets, chips, logs and other organic materials, they offer:
- Reduced carbon footprint compared to oil/gas boilers
- Renewable energy source
- Lower emissions of pollutants
- Efficient, sustainable low-maintenance heating
For Businesses:
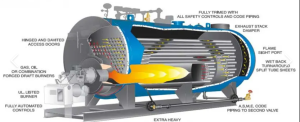
Commercial biomass steam boilers help reduce carbon footprint, lower electricity costs and produce clean thermal energy. Used in both public and private industrial settings, large 500 MWth boiler plants can achieve heating efficiency up to 89%.
Combustion Process:
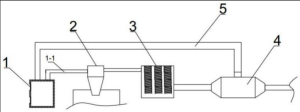
The commercial combustion process builds on four main units:
- Feed system
- Combustion chamber
- Air supply
- Emissions system
Industrial settings often add gas recirculation (FGR), automatic controllers and separate heat exchangers.
Factors Affecting Biomass Boiler Efficiency
1. Flue Gas Temperature
The difference between initial temperature and flue temperature indicates efficiency. Hot exiting gases mean heat wasn’t transferred to water, representing lost energy. Industrial installations often use maintenance devices to prevent such losses.
2. Type of Biomass Fuel
Typical biomass boiler systems average 80-90% efficiency, depending on fuel type. Here’s a breakdown of common fuels:
| Fuel Type | Energy per Ton (Moisture Content) |
|---|---|
| Wood chips | ~4800 kWh (10-15%) |
| Logs | ~3500 kWh (25-30%) |
| Wood pellets | ~4800 kWh (5-8%) |
| Sawdust | ~1500 kWh (<20%) |
3. Emission Levels
Lower emissions generally indicate better heating efficiency. Commercial biomass boiler emissions fall into three categories:
CO₂ Emissions
While wood combustion produces high CO₂ due to high calorific value, biomass emissions are part of natural atmospheric carbon cycle, making the fuel carbon neutral.
NOₓ Emissions
Small dry pellets typically emit 50-60 mg/MJ, while chip boilers emit 170-180 mg/MJ. Both levels are negligible for maintaining efficiency.
Particulate Matter (PM)
Modern industrial biomass boilers produce 10-70 mg/MJ, similar to oil. Ceramic filters help maintain low emissions, especially in urban areas.
Thermal Storage Capacity
Thermal storage allows boilers to store heat energy, extending working life. High storage means better heating efficiency and lower emissions. Studies show:
- 25 KW modern biomass boilers with buffer tanks achieve 74% efficiency
- Same boilers without buffers achieve only 57% efficiency
However, separate buffer containers increase the already substantial system size.
Biomass Boiler Costs
Installation Costs
Purchase and installation costs can be high, especially for residential use:
- 15kW automatic feed boiler: $16,000-$18,000
- 15kW manual feed boiler: $11,000-$13,000
Fuel Costs
Wood pellets cost $200-$300 per ton, with annual residential fuel costs around $3,000.
Maintenance
Maintenance costs are minimal but important:
- Weekly ash removal (or invest in self-cleaning models)
- Feed system maintenance every two months
- Weekly heat exchanger and ash remover cleaning
- Annual technician inspection
How to Get Biomass Boiler Grants
- Research available grants and eligibility requirements
- Contact relevant agencies (local councils, energy companies, government departments)
- Complete application with all required documentation
- Submit application and await response (typically within weeks)