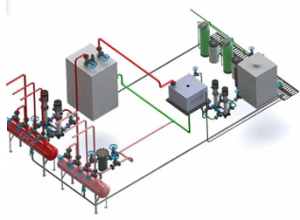
Understanding Energy Efficiency in Boilers
Energy efficiency has become a fundamental characteristic of modern boiler systems. But what exactly does “energy efficient” mean in industrial boiler context?
An energy efficient boiler maximizes output while minimizing energy input. Some boilers may use more energy to generate heat but less to transfer it, while others might generate heat efficiently but lose energy during transfer. The most efficient systems optimize both generation and transfer processes.
Steam Boiler Systems
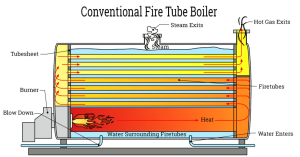
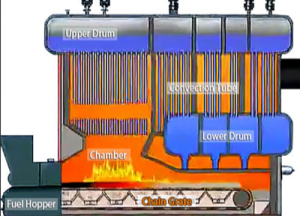
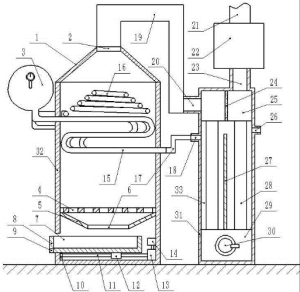
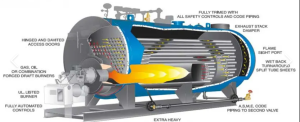
Steam boilers generate energy by heating water beyond its boiling point, converting liquid water into steam. The steam then transfers heat throughout the system.
Advantages:
- Excellent heat transfer capabilities
- Well-established technology with widespread industry knowledge
- Suitable for applications requiring large amounts of instantaneous energy
Disadvantages:
- Prone to corrosion from oxygen, foaming water, and reactive waste
- Mineral deposits and scale buildup reduce efficiency over time
- Requires regular maintenance and water treatment
- Vulnerable to freezing in cold conditions
- Operates under high pressure, requiring safety precautions
Thermal Oil Heater Systems
Thermal oil heaters generate energy from hot combustion byproducts firing over a helical coil. The system heats fluid through particle emission and convection, circulating it in a closed loop without phase change.
Advantages:
- Operates at high temperatures with low pressure
- No corrosion issues (closed system with no water)
- No mineral deposits or scaling
- Resistant to freezing temperatures
- Doesn’t require water treatment or steam traps
- Generally safer with lower explosion risks
Disadvantages:
- Higher flue gas temperatures indicate some energy loss
- Less suitable for applications needing instantaneous large energy bursts
Key Efficiency Comparison Factors
1. Corrosion Resistance
Steam boilers are prone to corrosion from water and chemicals, while thermal oil systems are completely non-corrosive. Corrosion significantly impacts energy efficiency by degrading components over time.
2. Performance in Cold Conditions
Steam boilers require frequent winter maintenance and are vulnerable to freezing damage. Thermal oil systems perform reliably in cold weather without special precautions.
3. Operating Pressure
Steam systems generate high pressure that increases exponentially with temperature, requiring safety measures and dedicated operators. Thermal oil systems operate at low or no pressure, reducing risks and operational costs.
4. Operating Temperature
While thermal oil systems can operate at higher temperatures (typically around 300°C for organic oils), they have higher flue gas temperatures (~350°C) compared to steam systems (~200°C), indicating greater heat loss.
Technical Specifications Comparison
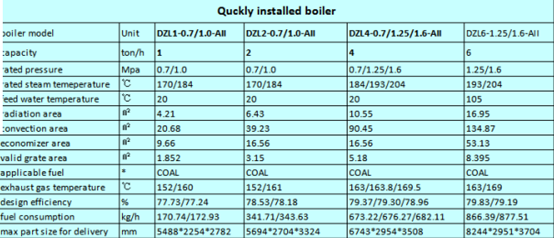
Steam Boiler Specifications
| Boiler Model | Capacity (ton/h) | Rated Pressure (MPa) | Steam Temperature (°C) | Design Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZL6-1.25/1.6-AII | 6 | 1.25/1.6 | 193/204 | 80.11/79.44 |
| SZL10-1.25/1.6-AII | 10 | 1.25/1.6 | 193/204 | 80.55/80.28 |
| SZL20-1.25/1.6-AII | 20 | 1.25/1.6 | 193/204 | 81.09/80.77 |
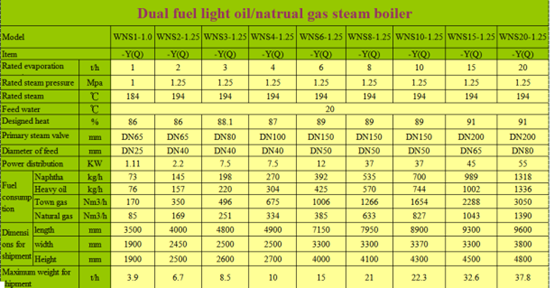
Thermal Oil Heater Specifications
| Model | Rated Power (KW) | Thermal Efficiency (%) | Design Pressure (MPa) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Y(Q)L)(W)-120-YQ | 120 | ≥75% | 1.0 | 350 |
| (Y(Q)L)(W)-1000-YQ | 1000 | ≥75% | 1.0 | 350 |
| (Y(Q)L)(W)-3500-YQ | 3500 | ≥80% | 1.0 | 350 |
Which System is More Energy Efficient?
After comparing both systems, thermal oil heaters generally demonstrate better energy efficiency due to:
- Ability to operate at high temperatures with low pressure
- Superior performance in extreme conditions
- Corrosion resistance that prevents energy loss
- Lower operational pressure reducing energy requirements
However, steam boilers remain preferable for applications requiring large instantaneous energy output. The optimal choice depends on your specific operational requirements and conditions.
Why Choose Boiler Philippines?
Boiler Philippines offers both high-quality steam boilers and thermal oil heaters with these advantages:
- Advanced regulation mechanisms for optimal heat efficiency
- Compact designs that save space while maximizing efficiency
- Automated detection, regulation, and alarm systems
- Simplified heating systems that reduce maintenance requirements
- Efficiency-promoting coil structures and heating surfaces
- Air-preheaters that boost overall system efficiency
Our technical team can assess your specific needs to recommend the most energy-efficient solution for your application.