Want to understand how industrial hot water boilers work and how they can benefit your business? Look no further! In this comprehensive article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about industrial water boilers, including their efficient working principles and the various types available.
You’ll also discover the advantages of hot water boilers, including lower costs and higher system efficiency. We’ll explore their diverse applications in sterilization and industrial water heating.
Industrial Hot Water Boiler Systems
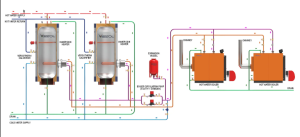
In simple terms, a hot water boiler system heats water for industrial or domestic use. The boiler uses electricity, natural gas, or oil to heat water, which is then distributed through pipes to where it’s needed.
Because hot water boiler systems have small storage tanks, they’re often paired with tankless water heaters. This combination ensures hot water availability without maintaining large reserves of heated water.
How Do Hot Water Boilers Work?
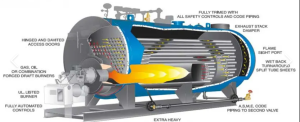
Industrial hot water boilers are constructed similarly to steam boilers but operate with water levels and steam space rather than being partially filled with water.
Burners fire into the boiler’s furnace and tubes to heat water inside the boiler shell. With the help of circulation pumps and piping, hot water is delivered to the process and then returned to the boiler for reheating. To prevent corrosion, any water loss must be replaced with chemically treated fresh water.
Additionally, boiler pressure vessels are typically horizontal, enclosed, insulated cylindrical tubes. Most industrial hot water boilers have two or three passes, each consisting of a unique piping system through which hot flue gases travel before turning inside the boiler.
Industrial Water Boiler Types
Let’s examine the available hot water boiler types in more detail.
1. High-Temperature Hot Water Boiler (HTHW)
These boilers operate at temperatures above 350°F with typical maximum working pressures below 300 PSIG. HTHW systems are ideal for large systems like district and campus heating due to their large size, high heat load capacity, and extensive piping networks. They’re also perfect for large process applications with high-temperature requirements that other boilers can’t meet.
2. Medium-Temperature Hot Water Boiler (MTHW)
These boilers operate between 250°F and 350°F with maximum working pressures of 150 PSIG. Systems using these boilers include campus and district energy loops, as well as apartment/hotel complexes and small processes.
3. Low-Temperature Hot Water Boiler (LTHW)
These systems provide temperatures below 250°F with maximum working pressures below 30 PSIG. LTHW boilers are often used in smaller structures including homes, where radiators distribute heat to various spaces.
Industrial Hot Water Boiler Advantages
As an industrialist, your primary goal is to improve boiler efficiency while reducing operating costs. Industrial hot water boilers deliver these benefits:
1. Lower Initial Equipment Costs
HTHW boilers have simpler designs and require fewer boiler room components, resulting in lower upfront investment costs. They’re also easier to install and maintain compared to other systems.
2. Reduced Operating Costs
HTHW boilers eliminate losses associated with steam boilers (steam traps, leaks, vents, and blowdown), helping lower ongoing operational expenses. They’re also less affected by temperature and pressure drops, resulting in additional operational savings.
3. Higher System Efficiency
HTHW systems efficiently handle high load spikes due to their large heat storage capacity. This means burners operate more evenly and effectively, resulting in higher overall system efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
4. Elevation Changes Don’t Affect System
Unlike steam systems, HTHW boilers use circulation pumps that overcome total system losses, making elevation differences largely irrelevant to system performance. This creates a more versatile and reliable heating solution.
Industrial Water Boiler Applications
Various industries use industrial commercial hot water boiler systems to simplify heating processes:
1. Sterilization
The high temperature of hot water efficiently destroys bacteria, making it ideal for sterilizing hard surfaces in:
- Food processing facilities
- General industry sections requiring facility, equipment, counter, and floor cleaning
2. Industrial Water Heating
Heated water is used in various industrial processes like mixing, curing, and cleaning, facilitating product manufacturing and maintaining sterile environments in:
- Bottle cleaning facilities
- Vehicle and truck washes
- Construction sites
- Gypsum plants
- High-volume facilities like hotels and hospitals
Industrial Water Boiler Fuel Types
1. Gas
Due to its efficiency and cleanliness, gas is the most popular fuel for hot water boilers. It generates less waste than other “dirty” energy sources, making it the preferred boiler fuel.
2. Oil
Oil requires pumping into tanks or delivery by tanker truck, making it a more expensive option. It also needs regular maintenance and inspections as undiscovered leaks can cause significant damage.
3. Electricity
Electricity eliminates the need to store or handle fossil fuels and requires less maintenance than oil or gas systems, making it a popular hassle-free heating solution.
Industrial Water Boiler Lifespan
The typical lifespan of an industrial hot water boiler is 10-20 years, though this varies depending on maintenance and usage conditions.
Signs Your Boiler Needs Replacement
1. Water Leaks
Check for leaks from the unit’s bottom or pipe connections. Address any leaks promptly to prevent further damage.
2. Insufficient Hot Water
If your boiler struggles to meet your facility’s hot water demand, it might need replacement or upgrades.
3. Wear and Tear
While hot water boilers have few moving parts, significant wear might justify replacing them with energy-efficient tankless units that require less maintenance and offer long-term savings.
Difference Between Steam Boilers and Hot Water Boiler Systems
Steam boilers and hot water systems differ in several ways. Steam boilers are categorized by pressure (>15 PSIG or ≤15 PSIG), while hot water boilers are categorized by temperature (HTHW, MTHW, LTHW).
Hot water boilers operate at lower pressures than steam boilers and use circulation pumps rather than natural convection. They also have different applications: steam boilers are better for humidification, direct injection, and heat exchangers, while HTHW boilers excel at district and campus heating.
Hot Water Boiler Pricing
Industrial water boiler costs depend on size and features. A new 1000 kW hot water boiler with a 20-year warranty typically costs between $10,000 and $30,000. While the initial investment may seem significant, these boilers save money long-term through reduced repair and replacement costs.
Final costs vary based on size, features, and installation charges. Purchasing energy-efficient models that consume less fuel can qualify you for state government tax credits while lowering operational expenses.
Conclusion
Industrial water boilers offer unique features and benefits you won’t find in many other systems. With three boiler types to choose from, they deliver lower prices, reduced operating costs, higher energy efficiency, and pollution-free operation. When purchased from a reputable source, industrial water boilers offer long lifespans that can make your business more profitable and hassle-free.
Take this opportunity to enhance your business operations! Contact us today to begin your journey toward a greener, more efficient future with our cutting-edge industrial water boilers.